Calculate Transistor Parameters
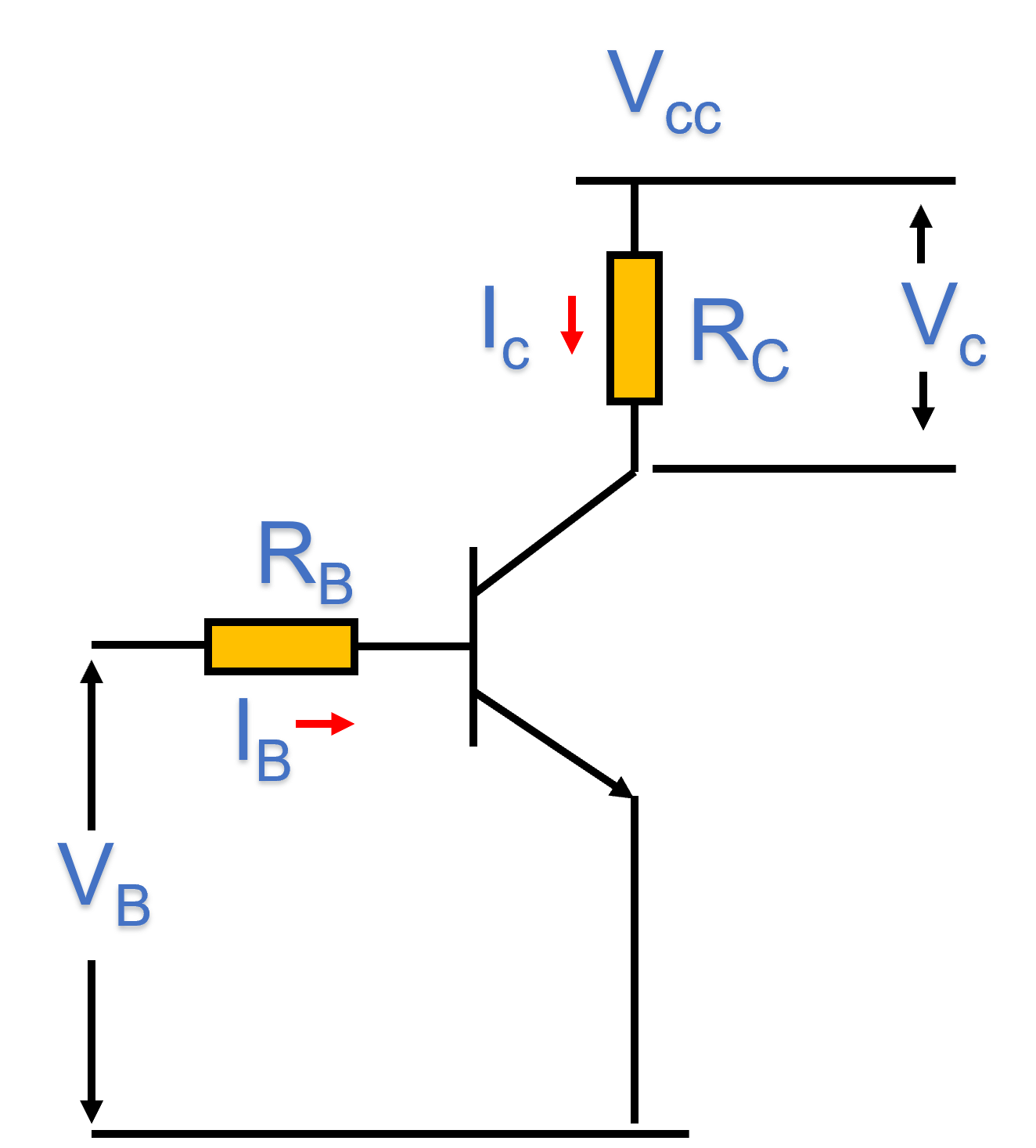
Figure 1: Transistor Schematic Diagram
Transistor Calculation Basics
1. Base Current (IB):
Base current (IB) is the current flowing into the base of the transistor. It is determined by Ohm's Law, where the base voltage (VB) is divided by the base resistance (RB):
IB = VB / RB
2. Collector Current (IC):
Collector current (IC) is the current flowing through the collector of the transistor. It depends on the collector voltage (VC) and collector resistance (RC):
IC = VC / RC
3. Beta (β) Value:
Beta, or current gain, (β) of a transistor is the ratio of collector current (IC) to base current (IB):
β = IC / IB
It indicates how much the collector current amplifies the base current.
Example Calculation:
Assume:
VB = 1.5V
RB = 10kΩ (10,000 ohms)
VC = 5V
RC = 2.2kΩ (2,200 ohms)
1. Calculate Base Current (IB):
IB = VB / RB = 1.5 / 10000 = 0.00015 A = 150 µA
2. Calculate Collector Current (IC):
IC = VC / RC = 5 / 2200 = 0.00227 A = 2.27 mA
3. Calculate Beta (β) Value:
β = IC / IB = 0.00227 / 0.00015 ≈ 15.13
Therefore, for this example, the transistor has a β value of approximately 15.13, meaning the collector current is about 15 times the base current.
Understanding these parameters allows engineers and hobbyists to effectively use transistors in various electronic applications, ranging from simple switching circuits to complex amplifiers and logic circuits.